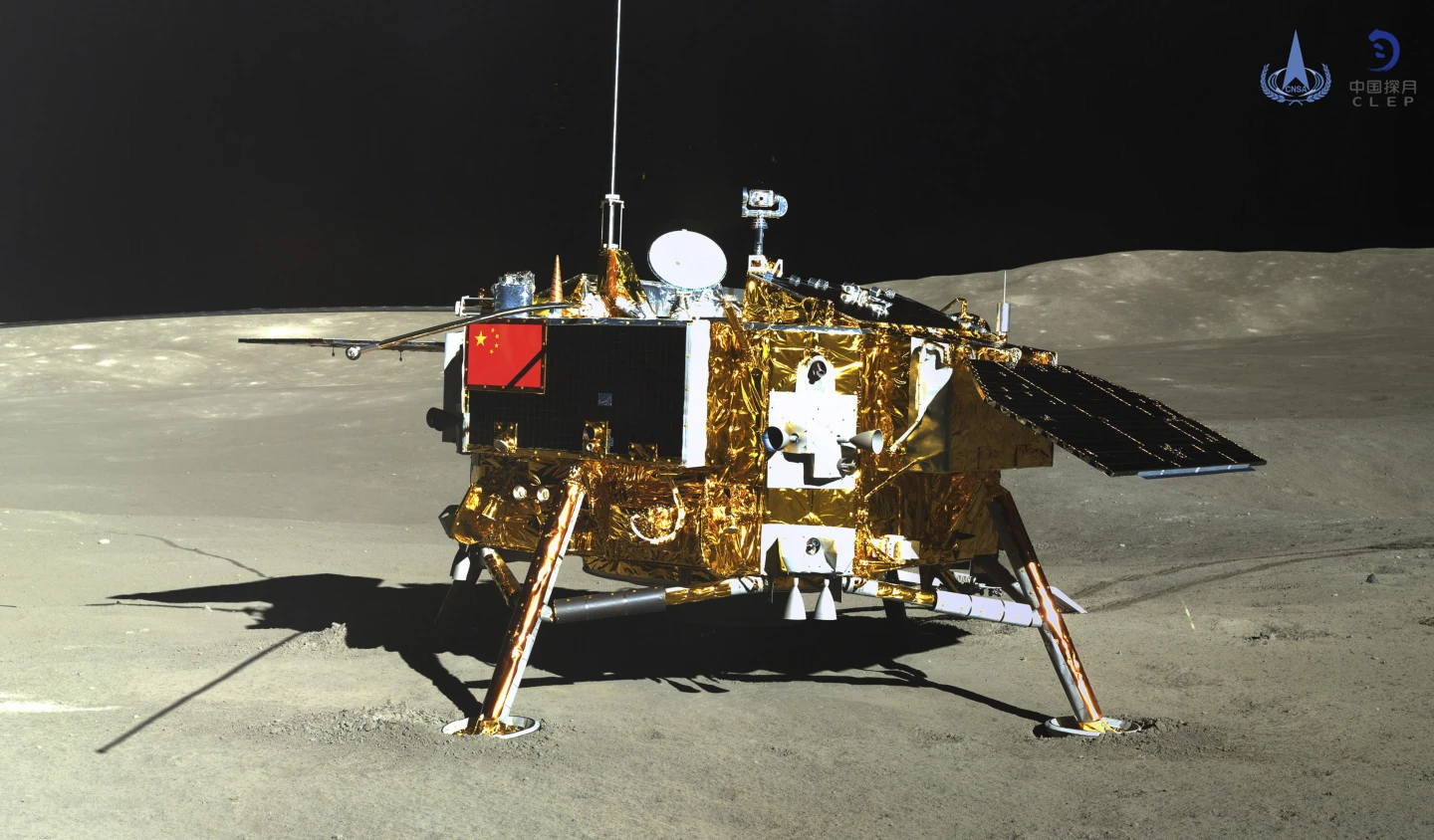
China says a spacecraft carrying rock and soil samples from the far side of the moon has lifted off from the lunar surface to start its journey back to Earth.
The ascender of the Chang’e-6 probe lifted off Tuesday morning Beijing time and entered a preset orbit around the moon, the China National Space Administration said.
The Chang’e-6 probe was launched last month and its lander touched down on the far side of the moon Sunday.
Xinhua News Agency cited the space agency as saying the spacecraft stowed the samples it had gathered in a container inside the ascender of the probe as planned.
The container will be transferred to a reentry capsule that is due to return to Earth in the deserts of China’s Inner Mongolia region about June 25.
Missions to the moon’s far side are more difficult because it doesn’t face the Earth, requiring a relay satellite to maintain communications. The terrain is also more rugged, with fewer flat areas to land.
Xinhua said the probe’s landing site was the South Pole-Aitken Basin, an impact crater created more than 4 billion years ago that is 13 kilometers (8 miles) deep and has a diameter of 2,500 kilometers (1,500 miles).
It is the oldest and largest of such craters on the moon, so may provide the earliest information about it, Xinhua said, adding that the huge impact may have ejected materials from deep below the surface.
The mission is the sixth in the Chang’e moon exploration program, which is named after a Chinese moon goddess. It is the second designed to bring back samples, following the Chang’e 5, which did so from the near side in 2020.
The moon program is part of a growing rivalry with the U.S. — still the leader in space exploration — and others, including Japan and India. China has put its own space station in orbit and regularly sends crews there.
The emerging global power aims to put a person on the moon before 2030, which would make it the second nation after the United States to do so. America is planning to land astronauts on the moon again — for the first time in more than 50 years — though NASA pushed the target date back to 2026 earlier this year.